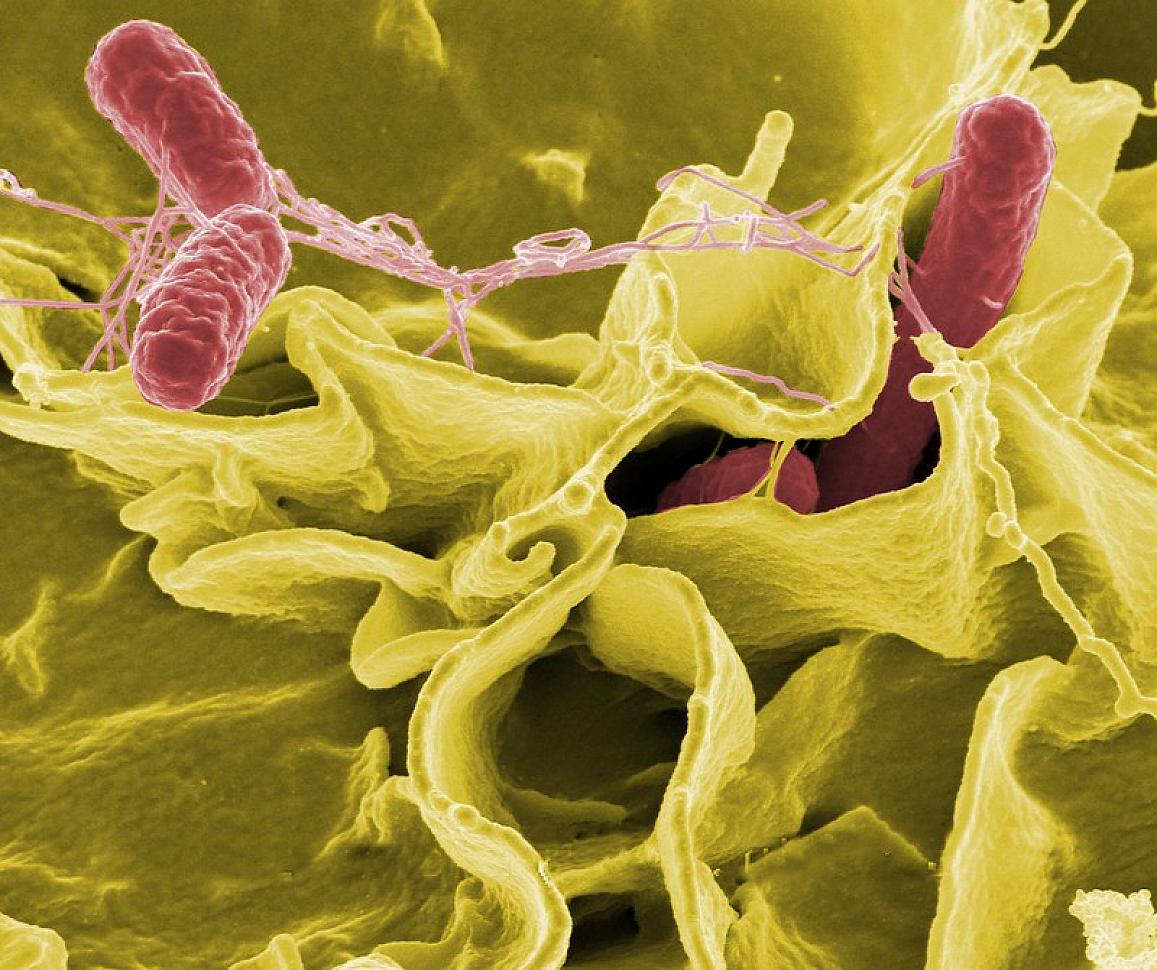
Salmonella (non-typhoidal) is a gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria that belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. it is considered one of the common and top causes of food poisoning and diarrhoeal diseases. The two major known types of Salmonella are Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. Salmonella are pathogens with intracellular properties. The illness caused by Salmonella is called as Salmonellosis.
The symptoms including fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting can characterize salmonellosis. Salmonella‘s survival character is unique for its spreading capability as it can survive several months in water and several months on a dry surface.
Salmonellosis
Salmonella infection or Salmonellosis is a common bacterial intestinal tract disease. These bacteria usually have habitation in the animal and human intestines which can be released through fecus. Humans are vulnerable to Salmonellosis through contaminated food or water. The symptoms of the disease usually show within the first 8 to 72 hours. In some people, the absence of the symptoms was also noticed. The lethality of the infection always depends upon the normal health of the infected individual. Most of the healthy individuals recover within days with or without medical observation.
Symptoms of Salmonellosis
When a Salmonella bacteria invades the body, many of the symptoms are expressed as its reaction, they are as follows:
1. Diarrhea with fever (<102°F)
2. Bloody stools
3. Nausea
4. Prolonged vomiting
5. Dehydration
6. Headache
The initial symptoms will be seen within 8 to 72 hours after the initial invasion of the bacteria.
Also read| Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) – Overview [PDF]
Causes of Salmonella Infection
Salmonellosis can generally spread through contaminated food and water. The food materials include chicken, beef, pork, eggs, fruits, and more. The CDC reported that the Salmonella outbreaks sickened people through dough, peanut butter, onions, pre-packaged salads, etc. The other reason for the spread is directly from the animal during contact, and also through contaminated water.
Food as a cause
Salmonellosis can occur through different types of contaminated food. These include:
- Raw eggs along with or without shells
- Spoiled fruits and vegetables
- Raw seafood, chicken, and red meat
- Milk and Milk products made unpasteurized
- Untreated water from any source
- Any food that is not properly refrigerated, cooked or heated
You can get sick from contaminated chicken if it’s not cooked thoroughly. You can also get sick if its juices leak in the refrigerator or get on kitchen surfaces and then get on something you eat raw, such as salad.
CDC
Prevention
The spread of the Salmonella infection can be avoided with some dedicated attention.
Cleanliness is the primary objective to avoid any type of disease. Cleaning the hands with soap is essential after a person is in contact with an animal or raw meat. Then cleanliness should be ensured before contacting food. Any utensils that were in direct contact with the raw meat, egg, or any other, should be washed and cleaned properly before cooking. CDC recommends not washing raw chicken, red meat, or sea foods to wash before cooking. As it can cause spread of the bacteria to utensils and other foods.
Avoiding direct contact with cooked and uncooked food can reduce the spread of the bacteria. This can be executed by storing cooked and uncooked food in different locations, using separate utensils for cooked and uncooked foods. Avoid using the same cutting board for cooked and uncooked foods.
Cook the food at a sufficient internal temperature to reduce the existence of bacteria.
Perishable foods like milk, meat, and seafood should be refrigerated at appropriate cooling temperatures. Keep in mind to avoid direct contact between cooked and uncooked food.
Diagnosis
Salmonella can be identified through an affected person’s stool sample. It can be also detected using other samples including blood and body fluids.
In the case of widespread Salmonellosis, the authority can identify Salmonella through different food sample tests.
References
- WHO (2018, February 20). Salmonella (non-typhoidal). World Health Organization. Retrieved November 09, 2023, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal)
- CDC (2023, November 08). Salmonella. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved November 09, 2023, from https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/
- CDC (2023, June 5). Salmonella and Food. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved November 10, 2023, from https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/communication/salmonella-food.html
- Giannella RA. Salmonella. In: Baron S, editor. Medical Microbiology. 4th edition. Galveston (TX): University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; 1996. Chapter 21. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8435/
Author: Achuth B S
Last updated:
Graduated from the University of Kerala with B.Sc. Botany and Biotechnology. M.Sc. Biotechnology from the University of Kerala. Attended certificate course in Artificial Intelligence for Everyone from Deeplearning.AI, Influenza Prevention and Control from World Health Organization. Attended workshops related to Bioinformatics at the University of Kerala. 3 years of experience in website management. Experience in WordPress, Blogger, Google Analytics, and Google Search Console.