A microscope is a device used to visualize materials with a micro size that is not visible to the naked eye. The first microscope was invented by Zacharias Janssen. This type of microscope is called the light microscope as it uses visible light to illuminate the object. The light microscope can be sub-classified as a Simple microscope and Compound Microscope.
Simple Microscope
A simple microscope is a type of microscope that uses visible light as the source of illumination. It uses a single-lens system for magnification. It uses a single lens specifically a magnifying lens to get an image that must be virtual, enlarged, and erect. A convex lens is a magnifying lens used in this microscopic system. The major difference between a simple microscope and a compound microscope is that a compound microscope uses a multiple-lens system. Which means it has 2 or more lenses.
Components of a Simple Microscope
A simple microscope is composed of many parts. These are explained below
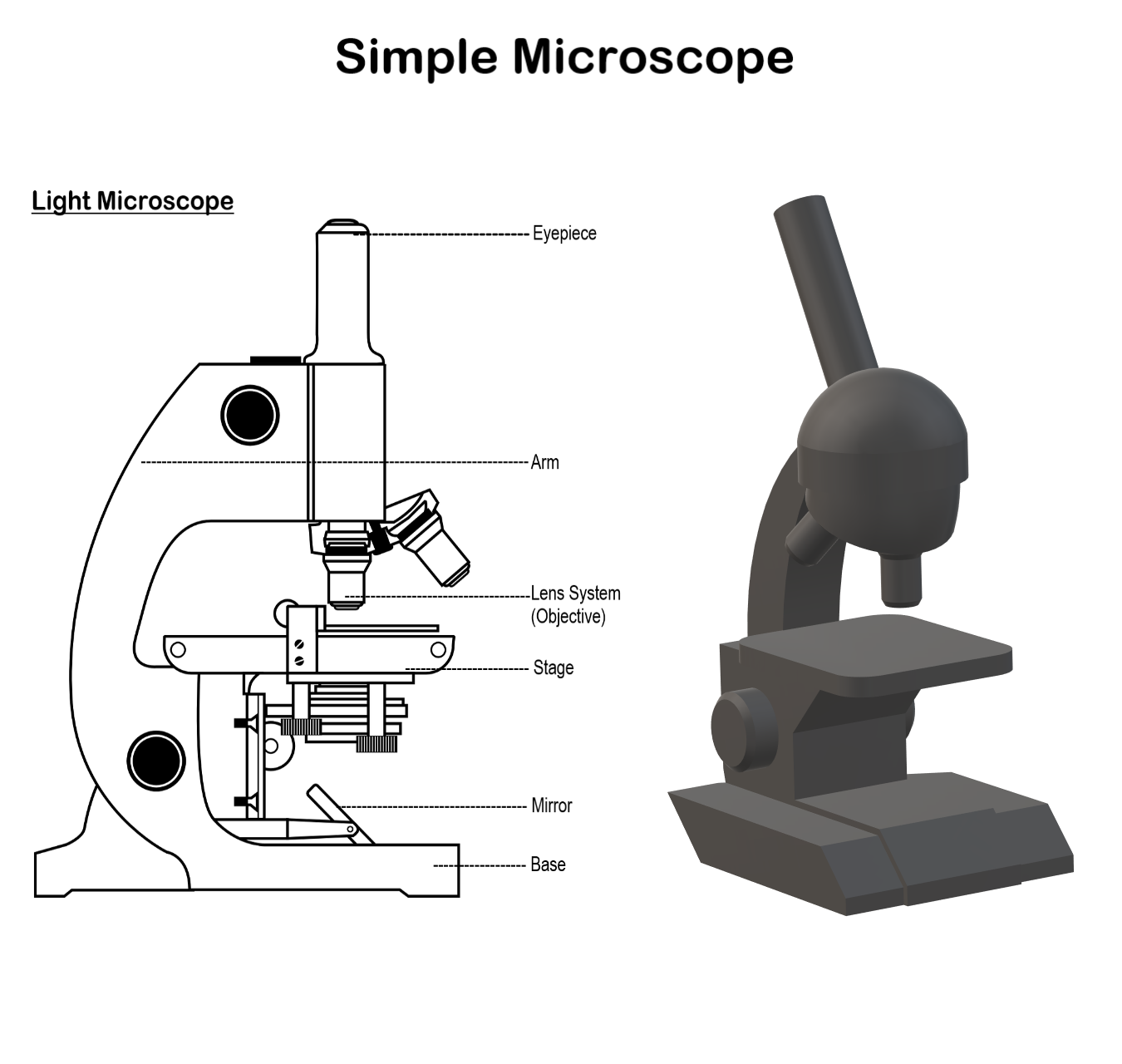
- Base: This is a metallic or a fibre part that acts as a stand to provide support for the microscope to stand erect.
- Stage: It is a plate-like metallic structure having a hole in the exact center which allows the passage of light to the optical system. This is the place where the specimen is placed and observed.
- Clips: Metallic clips can be present on the stage which helps to place the slides in the exact position.
- Mirror System: A concave mirror is attached below the stage on a frame. This mirror has a reflecting surface on the concave surface which captures and projects light to the specimen in the stage.
- Lens System: It uses a Convex lens, more specifically biconvex lens is used. It is fixed above the stage in a frame. It captures the light which is reflected on the specimen and magnifies the specimen. The enlarged image formed can be observed by keeping the eye above the lens system.
Magnifying Power (M) = 1+D/F
F = Focal length of the lens
D = Least distance of distinct vision for the normal eye
Applications
- Used to study biological specimens like algae, fungi, etc.
- Used in Pedology for soil sample observation.
- Used by dermatologists to observe skin samples for various skin diseases.
- Used by palaeontologists to observe fossil samples.
Published: 04/02/2023,1645
Last updated: