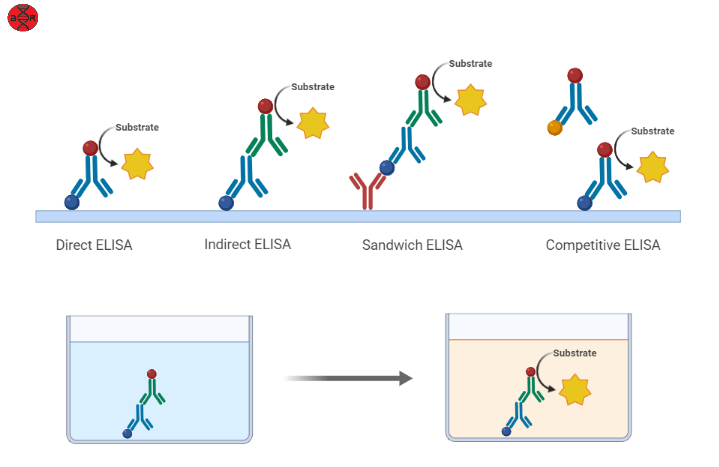
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, commonly known as ELISA
or EIA, a technique that depends on an enzyme. Both antigens as well as antibody
can be detected by conjugating an enzyme with an antibody that reacts with a
colourless substrate but generate a colour reaction. The colourless substrate
that generates colour upon a reaction as called as chromogenic substrate.
Several enzymes are used in ELISA that includes, alkaline phosphatase,
horseradish peroxidase, and β-galactosidase.
Different kind of ELISA techniques are there to detect
either antigen or antibody, which are; Indirect ELISA, Sandwich ELISA, and
Competitive ELISA.
INDIRECT ELISA
 |
| Cawang, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons |
Method used to detect antibody present in a sample (serum).
The ELISA plate is coated with antigen, to the antigen-coated microtiter wells
serum or any sample containing primary antibody is added. After incubation
period any free antibodies are washed away and the antibody bound to antigen is
detected using secondary antibody conjugated with enzyme. Again, after an
incubation period any free secondary antibody is washed away and a substrate
for the enzyme is added. The amount of coloured reaction product (OD) is
measured using ELISA reader that measures the absorbance of all the wells.
SANDWICH ELISA
 |
| Created with BioRender.com |
The presence of antigen in a sample is detected using this
Sandwich ELISA. Here in this method the microtiter wells are coated with
antibody and the sample containing antigen is added to the wells. After washing
the well to avoid any free antigen and enzyme conjugated secondary antigen is
added to this. The secondary antibody can bind specifically to a different
epitope in the bound antigen hence it is like a sandwich, and then substrate is
added and absorbance is measured using an ELISA reader.
COMPETITIVE ELISA
 |
| Created with BioRender.com |
Method to detect antigen in a different way in which to the
sample antigen antibody is added and allowed to react forming antigen-antibody.
The antigen-antibody complex is being added to the microtiter wells coated with
antigen. An enzyme conjugated secondary antibody is added, that can detect the
amount of primary antibody bound to the well like the indirect ELISA technique.
In the competitive assay if there is more amount of antigen in the original
sample, the lower will be the absorbance.
Qualified CSIR - National Eligibility Test (NET), eligible for Assistant Professorship in any Indian university. Graduated from the University of Kerala with B.Sc. Botany and Biotechnology. Attained Post-Graduation in Biotechnology from the Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Science (KUFOS) with the fourth rank. Conducted various seminars and presentations. Experienced in ELISA, Blotting, and other Good Laboratory Practices. Attended a certificate course in Patent Analytics. Done 6 months of internship in ICMR - Vector Control Research Center, Puducherry. 3 years of tutoring experience.